КОНЦЕПТЫ СТРАТЕГИЧЕСКОГО ПЛАНИРОВАНИЯ АГРОПРОДОВОЛЬСТВЕННОГО СЕКТОРА
КОНЦЕПТЫ СТРАТЕГИЧЕСКОГО ПЛАНИРОВАНИЯ АГРОПРОДОВОЛЬСТВЕННОГО СЕКТОРА
Аннотация
В связи с переходом от задач самообеспеченности к задачам по достижению физической и экономической доступности на уровне рациональных норм потребления требуются изменения концептуальных основ стратегирования агропрома. В статье рассмотрены проблемы встраивания в систему стратпланирования, действующих концептов Доктрины продовольственной безопасности. Предложено дополнить концепцию стратегического планирования развития агропродовольственного сектора положениями о единстве (конвергенции) физической и экономической доступности продукции. Введен в научный оборот конкретизированный научно-понятийный аппарат формирования концепции стратегического планирования с учетом задач в сфере обеспечения продовольственной безопасности (в части определений «физическая доступность продукции», «экономическая доступность продукции»). Это способствует постановке комплексной многоцелевой задачи в сфере развития АПК и обеспечения продовольственной безопасности и выработке релевантных методов ее решения.
1. Introduction
The 2020 New Doctrine introduces fresh directives aimed at guaranteeing food sovereignty, which involves making sure that all residents of a nation have both physical and economic access to food while maintaining food production at levels that do not compromise reasonable consumption standards. The correctness of the strategic task in this formulation is obvious. However, a change follows that the guidelines of the previous Doctrine (from 2010) regarding the transition of threshold indicators of self-sufficiency in some types of products were achieved only by reducing the level of domestic consumption per capita. In the case of products like fruits, vegetables, and meat, the per capita consumption level during the analyzed period rises primarily due to a decrease in product variety and a shift towards more affordable options such as apples, cabbage, and poultry .
Table 1 - Dynamics of self-sufficiency and level of consumption of main types of products per capita
Note: compiled by the authors based on [14]
Given that pandemics have introduced new challenges to addressing the increasingly complex issue of maintaining rational consumer production standards in the face of food problems, it becomes imperative to bolster a holistic structural framework for agricultural industry development and food security assurance.
2. Research methods and principles
The purpose of the study is to propose a conceptual framework for strategic planning for the development of the agri-food sector, taking into account modern national challenges in the field of ensuring food security.
Research objectives:
- to specify key concepts in the field of ensuring national food security that contribute to the formulation of a multipurpose task for the development of the agri-food sector;
- supplement the content of strategic planning of the agri-food sector with provisions on the convergence of aspects in the field of ensuring food security.
The study is based on the theory of strategic management and the concept of sustainable development of the agro-industrial complex.
The following information resources were used: (1) provisions of the Doctrine of Food Security of the Russian Federation of 2020; (2) Rosstat data on production and consumption per capita for 2017-2021.
To extract knowledge, the following methods were used: scientific generalization and critical analysis (assessment of key concepts in the field of ensuring food security), expert assessments (analysis and design of the conceptual framework for strategic planning for the development of the agri-food sector), comparative analysis (assessment of trends characterizing the dynamics of self-sufficiency, physical and economic product availability).
3. Main results
Before setting new goals for strategic plans, it is necessary to clarify the terminology of food security, since a number of controversial issues are revealed in relation to it:
First, the concept of “food sovereignty” is based only on self-sufficiency thresholds. However, as scientists note , , the current situation is not a guarantee of food independence, since increased self-sufficiency can be achieved with a decrease in domestic consumption, as is currently happening for milk. It is logical that if the rate of decline in production is lower than the rate of decline in its consumption, then there will be an increase in the level of self-sufficiency of this production.
Secondly, the concept of “physical accessibility...”, presented in the Doctrine, takes into account only the development of commodity-distributing employment and overlooks the possibility of creating rational consumption standards through the domestic production of food products, which precisely increase the requirements for the country’s food independence. Considering that the availability of products is influenced by both domestic production and imports, maintaining complete self-sufficiency in terms of physical availability for essential product categories is necessary to achieve food independence.
Thirdly, the concept of “economic accessibility...” refers only to product prices and loses sight of consumer income. Both play an important role in achieving affordability. The experience of the USA and the EU shows that even in conditions of high prices, it is possible to achieve a high solvent income for products.
The specified clarifications to determine key interpretations of concepts (Table 2).
Table 2 - Refined interpretations of aspects of food security
Note: compiled by the authors
Physical accessibility does not ensure economic accessibility; at the same time, the economic accessibility of products is an incentive for the formation of physical accessibility. Understanding this is important for creating conditions that ensure a balance between the sun and supply at the level of rational consumption standards and above.
Table 3 - Correlation of the level of production and consumption of products per capita with rational standards, coefficient
Note: compiled by the authors based on [14]
Today, the problem of food security and agricultural development requires a comprehensive approach. Each aspect of agricultural development creates the necessary conditions for the formation of an alternative aspect of food security. To ensure the physical availability of products, it is necessary to create conditions for the economic development of agriculture, to ensure the economic accessibility of products – real conditions for development, to ensure the quality and safety of products – conditions for the environmental development of the industry. This exactly corresponds to global concepts of agricultural development.
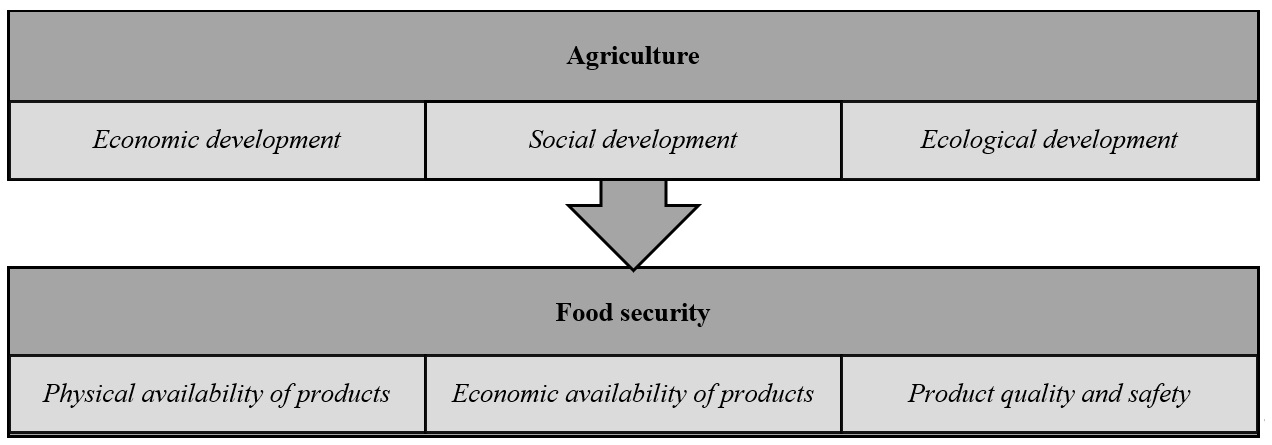
Figure 1 - National food security as a result of the development of domestic agriculture
1. To physically ensure the provision of products, a developed material, technical and technological base, a developed commodity distribution and rural infrastructure, high levels of profitability and profitability, ensuring payback of costly and reproductive resources, etc. are required.
2. To ensure economic accessibility, low prices for products and a high level of income of the population are necessary.
In this period, the food mission of agriculture respects: (1) high quality products and low costs for them, (2) low labor costs and decent wages, (3) low prices for products and high profitability with profitability. This concept is the fundamental principle of agricultural planning that must take into account all key aspects. The proposed concept of strategic planning in the field of development of the agricultural industry and ensuring food security based on the unity of physical and economic accessibility of products (Figure 2).
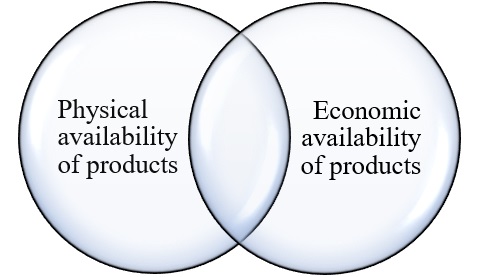
Figure 2 - Unity of food security aspects
In 2014, Russia adopted the Concept for the Development of Domestic Food Assistance . This concept aimed to guarantee both economic and physical access to food by either directly supplying food products to the less privileged citizens or furnishing them with the necessary financial resources to procure food. Unfortunately, as of now, the real-world implementation of this concept remains unrealized.
4. Conclusion
The modern problem in the field of food security is becoming complex, requiring solutions to problems both in the sphere of production and consumer products. To strengthen the theoretical and methodological positions of the Doctrine, the authors of the concept form the unity of the physical and economic accessibility of products, which represents the principal and fundamental basis for changes in planning. A possible practical option for implementing the concept involves returning to consideration of the draft Federal Law “On Food Security of the Russian Federation” . The authors of the developed mechanism for implementing the proposed concept and carried out a financial and economic justification were the absence of the main reason for the violation of the law of the State Duma of the Russian Federation, which is in the second reading.
